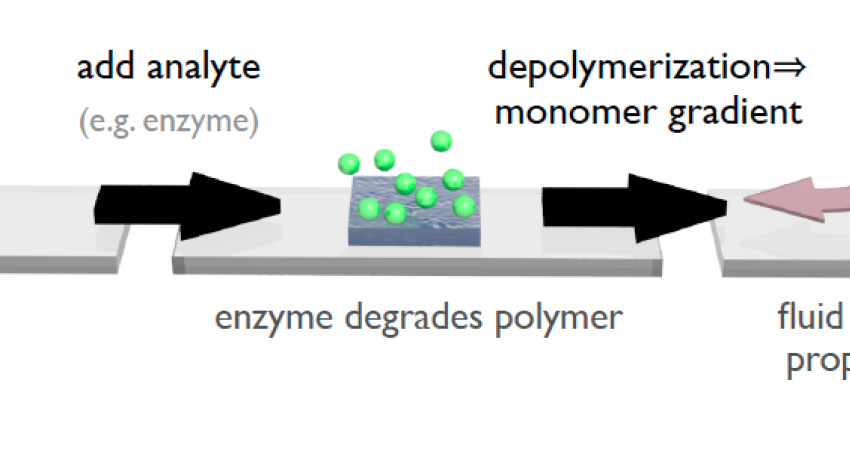
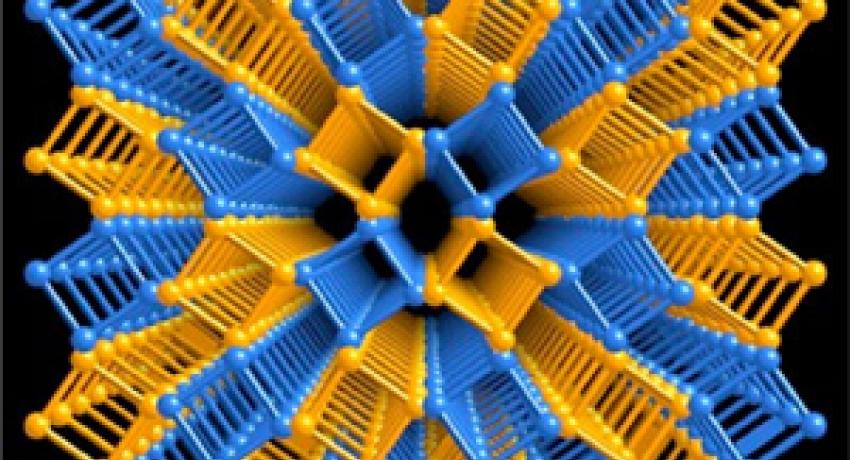
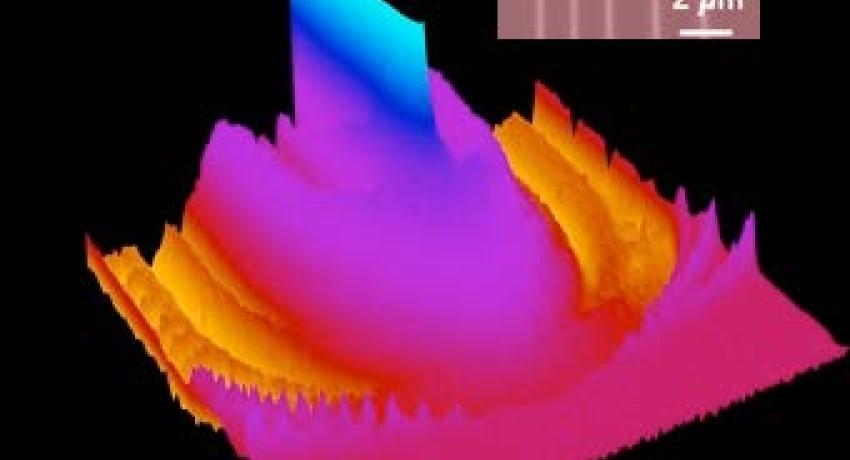
Low--Loss Zero--Index Metamaterial in the Near--Infrared
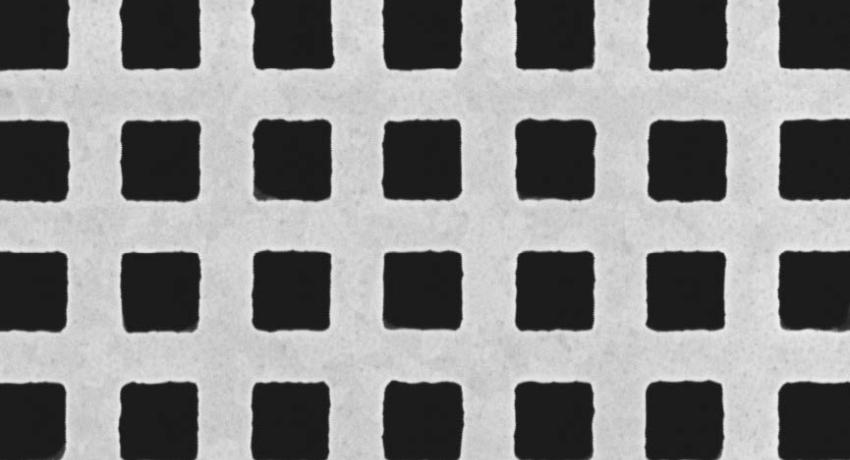
The novel properties of meta-materials enable new technologies such as electromagnetic cloaks, flat near- and far-field focusing lenses, and transformation optics devices. MRSEC researchers’ nature-inspired design techniques and accurate fabrication methods minimize loss in this polarizationinsensitive free-standing gold-polyimide-gold meta-material which has both a zero refractive index and high transmission at 1.5μm. The vertical sidewalls eliminate bianisotropy. Low-loss meta-materials could enable a new generation of practical optical devices